Everything is “data-driven” these days. Data-driven marketing, data-driven management, data-driven business decisions — information is truly power for organizations.
And to harness the full potential of data, businesses need to understand what’s called the data lifecycle — the stages that data passes through.
The data lifecycle comprises eight stages. We’ll explain each one, who is involved, and show how AI and/or agentic AI can be applied across the cycle. We’ll also provide concrete examples through the lens of a sample project involving customer sentiment analysis.
In this sample project, Company X wants to analyze customer sentiment from social media to improve its customer service approach.
What is the data lifecycle?
The data lifecycle encompasses a series of eight stages through which data passes — from its creation to its end use in decision-making. Each stage involves specific processes and stakeholders that ensure data is properly managed, analyzed, and utilized.
Understanding the data lifecycle helps organizations optimize their data-handling practices. This leads to better data quality, improved security, and smarter business decisions. By effectively navigating these eight stages, organizations can transform raw data into information they can really use to drive innovation.
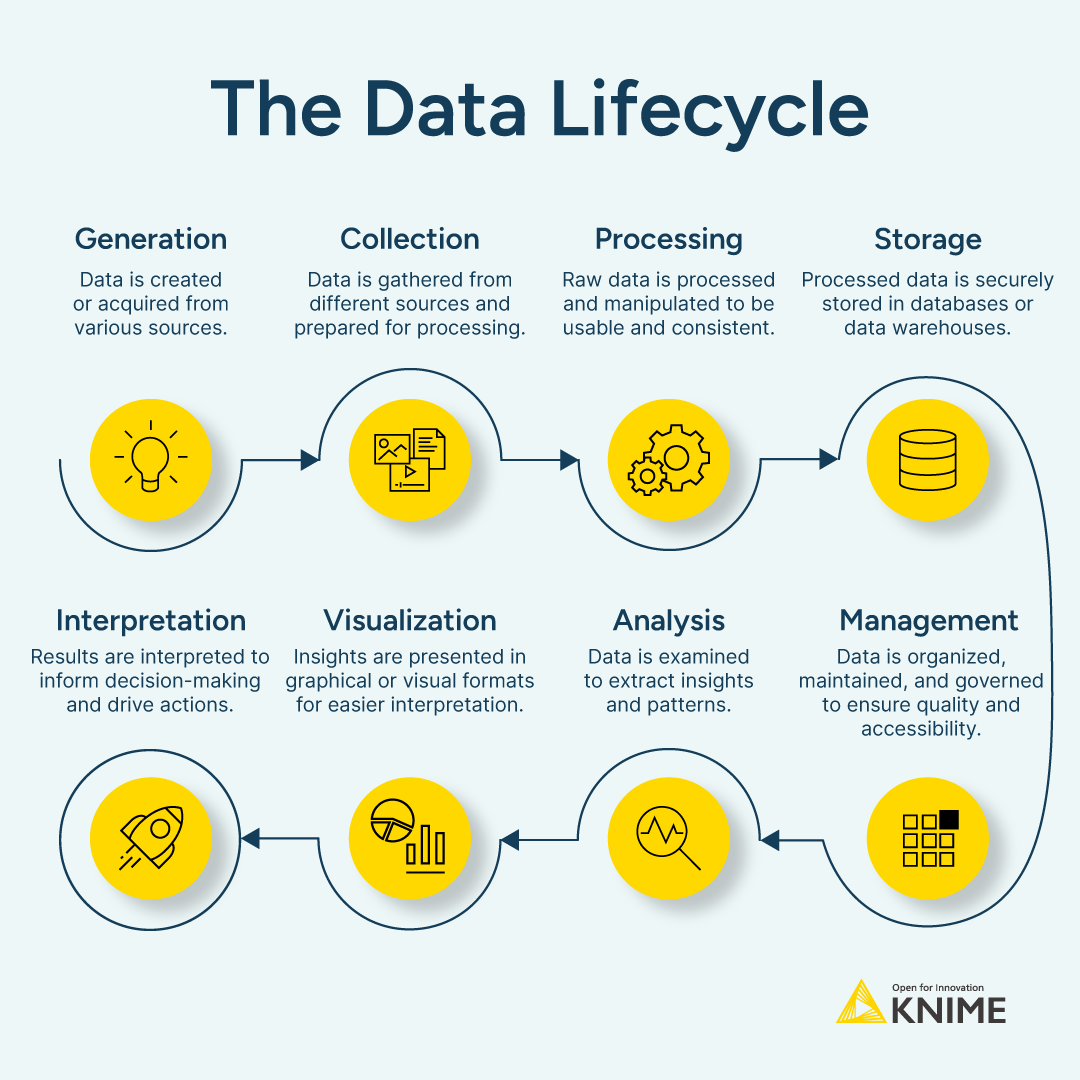
What is the AI-Enabled Data Lifecycle?
Understanding how both AI and agentic AI interact with each stage of the data lifecycle enables organizations to unlock better quality, smarter automation, and faster time to value from their data assets.
Here are some examples:
- AI-Augmented Data Generation & Collection: AI can generate domain-specific synthetic data (e.g. conversations, customer data) for example, to overcome data scarcity or avoid exposing private data.
- AI in Processing & Quality: Machine learning and LLMs can automate data cleaning, anomaly detection, and classification, reducing manual preprocessing efforts.
- AI-Driven Storage Optimization: AI can dynamically tier storage based on predicted future usage, query patterns, or compliance needs.
- AI-Enhanced Insights: Predictive and prescriptive models (including agentic AI) can go beyond descriptive analytics to suggest actions, detect trends, and forecast outcomes.
- AI-Powered Interpretation & Action: Intelligent systems can interpret results and suggest next steps, integrating outcomes into operational workflows.
Learn How to Go From Idea to AI Agent without Code
What are the 8 stages of the data lifecycle?
The data lifecycle can be broken down into eight distinct stages, each of which plays a vital role in transforming raw data into valuable insights. Understanding these stages helps organizations streamline their data processes — which helps ensure efficiency, accuracy, and security.
1. Data generation
Data generation marks the birth of the data lifecycle. This first stage involves the creation of data from a variety of sources, including:
- Customer interactions
- Business and financial transactions
- Social media activities
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
For example, a retail company might generate customer data from point-of-sale (POS) systems, e-commerce shopping carts, and feedback forms.
Who is involved in data generation?
The main roles typically involved in data generation include:
- Data engineers: Develop systems and execute processes for generating data.
- IT staff members: Build and maintain the technical infrastructure that supports data generation.
How can AI and/or agentic AI be used in data generation?
AI: AI can be used in data generation through generative models (like GANs, LLMs, etc.) to create synthetic datasets that reflect patterns in real data.These datasets are typically used in controlled settings like testing or experimentation, where using real data would raise privacy or compliance concerns.
Agentic AI: Agentic AI systems can monitor newly generated data for compliance with defined governance policies and surface potential issues early in the lifecycle.
Company X example: Data generation occurs when Company X derives new data assets, such as sentiment scores, engagement metrics, or topic labels, from customer interactions on social media. If privacy risks are identified, an agentic workflow can flag the issue and route the data through approved anonymization or synthetic-data pipelines before it is used.
2. Data collection
The second stage in the data lifecycle, data collection, involves the structured gathering of relevant data from a variety of sources like:
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Web scraping
- IoT sensors
- Application programming interfaces (APIs)
- Transaction records
- Social media monitoring
- Observations
This stage is critical to the process, as it ensures that the data needed for analysis is accurately aggregated and data loss is reduced.
Who is involved in data collection?
The main roles typically involved in data collection include:
- Business stakeholders: Ensure the data they need for decision-making is being collected.
- Data engineers: Integrate data from various sources into centralized databases.
How can AI and/or agentic AI be used in data collection?
AI: AI can improve data collection by automating the extraction of data from different sources (e.g. REST APIs, SaaS applications, or unstructured inputs), including filtering, classification, and deduplication to improve data relevance and quality.
Agentic AI: Agentic AI systems can orchestrate data collection across systems by proactively deciding what data it needs and then collecting that data.
Company X example: Data collection occurs when the business uses web scraping tools to collect data from social mentions and integrates it with customer purchase data collected via e-commerce platforms. AI can help identify which social mentions are most relevant to specific products or campaigns, while an agentic workflow ensures these sources are collected and refreshed consistently, with minimal manual intervention, including in quickly changing environments.
3. Data processing
Data processing is the third stage in the data lifecycle. It involves the following steps that prepare data for analysis:
- Data cleaning: Removing duplicate content, correcting errors, and filling in missing values.
- Data transformation: Converting raw or unstructured data into a suitable format or structure.
- Data integration: Combining data from disparate sources into a cohesive dataset.
- Data reduction: Simplifying datasets by eliminating redundant or irrelevant data.
- Data validation: Ensuring processed data meets organizational standards and accurately reflects its original sources.
These steps prepare collected data for meaningful analysis, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
Who is involved in data processing?
The main roles typically involved in data processing include:
- Data engineers: Develop ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines to automate processing.
- Data scientists: Explore raw data to determine useful sources and formats, informing the creation of pipelines.
How can AI and/or agentic AI be used in data processing?
AI: AI can support data processing by applying machine learning techniques to automate tasks such as data cleaning, deduplication, anomaly detection, and normalization across structured and unstructured data.
Agentic AI: Agentic AI systems can monitor data processing pipelines for data quality issues (for example, spikes in duplicates, schema changes, or failed validation checks) and remediate by choosing to rerun processing steps or take an entirely different approach.
Company X example: Data processing occurs when the business processes its social media data by removing repeated posts, comments, or identical reviews posted on different platforms. It also includes correcting inconsistencies in usernames or hashtags and standardizing date formats. An agentic workflow can monitor incoming data quality metrics in real-time and automatically rerun processing steps or choose how to escalate or act when there are problems.
4. Data storage
The fourth stage of the data lifecycle, data storage, is essential for ensuring data is accessible, safeguarded, and backed up for future use. This stage focuses on data privacy — configuring your storage solution for privacy — by securely storing processed data in:
- Databases
- Data warehouses
- Cloud storage solutions
- Data lakes
- On-location storage (e.g., physical servers)
This stage in the data lifecycle involves choosing the right storage solution for your data protection needs and organizing data for efficient retrieval and use.
Who is involved in data storage?
The main roles typically involved in data storage include:
- Database administrators: Manage data storage systems.
- IT staff and security teams: Ensure data security and backup protocols are in place.
How can AI and/or agentic AI be used in data storage?
AI: AI can support data storage by analyzing data access and usage patterns to recommend optimizations such as indexing strategies, partitioning schemes, or tiered storage to improve performance and reduce cost.
Agentic AI: Agentic AI systems can monitor storage usage, access patterns, and predefined compliance rules, and trigger approved actions such as adjusting retention periods, managing backups, or recommending changes to access controls within established policies.
Company X example: Data storage occurs when the business securely stores social engagement data like comments, captions, and reactions in cloud-based data warehouses. This enables easy access for analysis while facilitating scalability. An agentic workflow can adjust retention policies during active campaigns to keep relevant engagement data readily accessible, while archiving older or less-used data according to predefined rules.
5. Data management
Data management is the fifth stage in the data lifecycle. It encompasses the ongoing organization and maintenance of data through:
- Data governance: Establishing standards, defining user roles, and ensuring compliance. Setting policies for data sharing across departments.
- Data quality management: Monitoring, cleaning, and validating data.
- Data security: Implementing encryption and access controls and conducting security audits.
- Data access and retrieval: Setting up and using indexing and cataloging techniques.
- Data integration: Creating a unified view of data and ensuring consistency.
- Data archiving and deletion: Caching or deleting outdated or infrequently used data.
These processes ensure data remains accurate, accessible, and meets regulatory requirements. And, most importantly, ensures privacy while data is being used.
Who is involved in data management?
The main roles typically involved in data management include:
- Data engineers: Facilitate better decision-making by ensuring data is secure, accurate, and accessible.
- Database governance and security teams: Implement policies and data standards. Maintain data privacy.
How can AI and/or agentic AI be used in data management?
AI: AI assists with data management by continuously monitoring data quality, detecting inconsistencies, and supporting governance tasks such as classification and metadata enrichment.
Agentic AI: Agentic AI systems can coordinate data management activities across systems by monitoring compliance with defined policies, flagging potential risks (e.g. policy violations or quality degradation), and triggering approved remediation or review workflows.
Company X example: Data management occurs when the business puts policies in place that ensure customer data from sources like Facebook and Instagram is handled securely, regularly cleans and validates it, and archives old interactions. AI can help identify potential privacy or compliance risks in social data, while an agentic workflow ensures these governance rules are applied consistently across systems within defined guardrails.
6. Data analysis
Data analysis, the sixth stage in the data lifecycle, is where real value is discovered by using analytical tools and techniques to identify patterns, trends, and correlations in data. The key components involved are:
- Descriptive analytics: Summarizes past data to help organizations understand what has happened.
- Diagnostic analytics: Examines data to determine why certain events or issues occurred.
- Predictive analytics: Uses historical data and machine learning (ML) to forecast trends and future outcomes.
- Prescriptive analytics: Guides future actions by predicting optimal steps to reach a specific goal.
This stage makes it possible to extract meaningful insights from data so businesses can make more informed decisions.
Who is involved in data analysis?
Perhaps obviously, the main role involved in data analytics is a data analyst, who oversees some of this work. For more advanced tasks around predictive and prescriptive analytics, a data scientist is usually involved. Business stakeholders will also be included in data analysis processes so they’re able to ask questions and provide information about company goals. Other roles typically involved in data analysis include:
- Data analysts: Take on most data analysis tasks. For more complex tasks involving machine learning, they would rely on a data scientist.
- Data scientists: Facilitate better decision-making by ensuring data is secure, accurate, and accessible, and doing advanced data work like predictive and prescriptive analytics.
- Database governance teams: Implement policies and data standards.
How can AI and/or agentic AI be used in data analysis?
AI: AI accelerates data analysis through machine learning, natural language processing, and generative models that uncover patterns, predict outcomes, and generate insights at scale.
Agentic AI: Agentic AI can autonomously explore data, test analytical approaches, and surface recommended insights or next steps aligned with business objectives.
Company X example: Data analysis occurs when the business uses natural language processing (NLP) techniques to analyze social media sentiment and identify common themes in customer feedback. This allows Company X to create more targeted marketing campaigns. An agentic analytics workflow could autonomously evaluate campaign performance, highlight emerging customer concerns, and take appropriate action in real-time.
7. Data visualization
The seventh stage of the data lifecycle is data visualization. It involves representing data graphically to communicate data insights effectively. This is the stage in which complex data becomes more understandable through visualizations like:
- Charts and graphs
- Interactive and real-time dashboards
- Geospatial maps (e.g., heat and choropleth)
- Advanced techniques like scatter plots, histograms, and tree maps
Through graphical representations, this stage makes data understandable for organizational stakeholders and allows them to take action confidently.
Note: Although data visualization is the 7th step in the data lifecycle, a data analyst, data scientist, or data engineer, will likely refer to multiple types of visualizations in the exploratory stage of their analysis and perhaps even earlier in the process.
Who is involved in data visualization?
The main roles typically involved in data visualization include:
- Data scientists: Develop intricate visualizations to illustrate analytical models and outcomes and ensure they accurately reflect insights and trends.
- Business analysts: Use visualizations to present findings to stakeholders in an understandable format.
How can AI and/or agentic AI be used in data visualization?
AI: AI can support data visualization by recommending or generating charts, dashboards, and narrative summaries that highlight relevant patterns or anomalies for different users or roles.
Agentic AI: Agentic AI systems can monitor how dashboards are used and how underlying data changes, and trigger approved updates, such as refreshing views, adjusting thresholds, or sending alerts, based on predefined rules.
Company X example: Data visualization occurs when the business creates interactive dashboards that illustrate metrics like social shares, comments, and follower growth over time and heat maps that show regional social engagement levels across different locations. An agentic workflow can keep these dashboards up to date and notify relevant teams when negative sentiment increases in specific regions, based on defined alert thresholds.
8. Data interpretation
Data interpretation is the final stage in the data lifecycle. This is the stage in which the analyzed and visualized data is used to make informed business decisions. The key activities involved in this stage include:
- Reviewing dashboards, charts, and graphs to identify key insights.
- Making sense of analytical results and drawing conclusions to explain business performance.
- Suggesting actions based on data findings and providing strategic guidance on marketing, product development, and customer engagement.
- Presenting findings and using storytelling techniques to convey the significance of data insights.
This stage is important to an organization’s data usage practices, as it ensures that insights derived from data analysis and visualization are effectively utilized to drive strategic decisions and improve outcomes for an organization.
Who is involved in data interpretation?
The main roles typically involved in data interpretation include:
- Business analysts: Use visualizations to present findings to stakeholders in an understandable format.
- Stakeholders and executives: Make tactical decisions based on data.
How can AI and/or agentic AI be used in data interpretation?
AI: AI supports data interpretation by generating narrative explanations, summarizing insights, and simulating potential outcomes to support decision-making.
Agentic AI: Agentic AI can go further by triggering alerts, recommendations, or pre-approved workflows.
Company X example: Data interpretation occurs when business executives use the visualized social media data to refine customer service strategies and enhance overall customer satisfaction. They do this by focusing on areas with negative customer sentiment. An agentic system could recommend and help decide to launch targeted customer outreach when sentiment analysis indicates rising dissatisfaction.
Why is the data lifecycle helpful?
Understanding the data lifecycle and the data lifecycle management (DLM) process is essential to organizations for several reasons:
Efficient data management
Each stage of the data lifecycle ensures that data is handled properly, which reduces errors and enhances data quality for organizations. Structured processes allow for systematic data collection, storage, and maintenance, which reduces inaccuracies and inconsistencies and protects sensitive data.
Improved decision-making
Structured data processes lead to more reliable insights. By following a clear lifecycle, organizations can trust and use data that is relevant and accurate, which is vital for making informed strategic choices.
Regulatory compliance
Managing data and its deletion properly means ensuring compliance with security and privacy regulations, which mitigates risk for organizations. By adhering to these lifecycle stages, businesses can maintain audit trails, enforce data governance policies, and confirm that data handling practices meet legal requirements.
Resource optimization
Streamlined data processes save organizations time and resources, which improves overall business efficiency. Automating data handling tasks and maintaining well-organized data systems reduces the time and effort it takes to manually process data and correct errors.
Data consistency and reliability
Maintaining consistency in data handling makes data trustworthy, but in reality data sources or pipelines can change year over year, making it hard to compare apples to apples. Maintaining consistent data sources and pipelines is crucial for conducting accurate analyses and deriving insights that organizations can actually use in the long-term.
Enhanced collaboration
In order to promote effective communication and collaboration across teams and departments, everyone must understand their job within the lifecycle. When clear roles and responsibilities are established at each stage, it facilitates better teamwork and project coordination.
Scalability and flexibility
A well-defined data lifecycle allows organizations to scale their data operations efficiently as their data needs increase. It also provides the flexibility to adapt to new data sources and technologies, which helps to future-proof organizations’ data management strategies.
When organizations understand and implement the data lifecycle, they can optimize their data handling practices. This can lead to more comprehensive and effective data utilization, better customer retention, increased ROI, and a stronger competitive advantage.
Future of the Data Lifecycle with AI
As AI becomes increasingly embedded across the data lifecycle, the focus will shift from isolated automation tasks to end-to-end orchestration.
Here’s what to look out for:
- AI agents will support multiple lifecycle stages by coordinating tasks and workflows across systems, rather than operating in isolation.
- Governance, transparency, and accountability will become even more critical as AI systems trigger actions with greater autonomy.
- Feedback loops between humans and AI will mature, allowing systems to improve over time while keeping humans in control of key decisions.
Data Lifecycle FAQ
Here are a few frequently asked questions and answers about the data lifecycle.
What is the First Stage of the Data Lifecycle?
The first stage of the data lifecycle is data generation. This is the stage in which data is created within various sources.
Why is Data Processing Important?
Data processing is important because it ensures that raw data is cleaned, transformed into suitable formats, and organized properly so it’s ready for accurate analysis.
What are the 5 Stages of the Data Lifecycle?
Although different organizations combine certain steps and list different numbers of data lifecycle stages, we define it within eight stages:
- Data generation
- Data collection
- Data processing
- Data storage
- Data management
- Data analysis
- Data visualization
- Data interpretation
What Do You Mean by Data Life Cycle?
The data life cycle is an 8-stage process that guides the creation, management, analysis, and utilization of data to ensure its accuracy, protection, and usefulness in decision-making.
Learn More About the Data Lifecycle
The data lifecycle is a comprehensive framework that guides the management and informed use of collected information, from data creation to its final utilization in business decision-making. By understanding and effectively implementing each stage, organizations can unlock their data’s potential and put it to work for them.
KNIME Analytics Platform supports each stage of the data lifecycle and can make data management and interpretation more accessible and efficient for businesses of all kinds.
